Loading

What is SQL? SQL stands for Structured Query Language. It is used to store information in databases which consist of tables that are collections of records or entities, organized into rows and columns. SQL is the tool that allows you to interact with this data. SQL is relevant in modern technologie...

What is a Database? A database is an organized collection of structured data designed to store information and make it easier to manage data efficiently. Modern database systems are built to store data, process transactions, and ensure data security while supporting a wide range of applications. Dat...
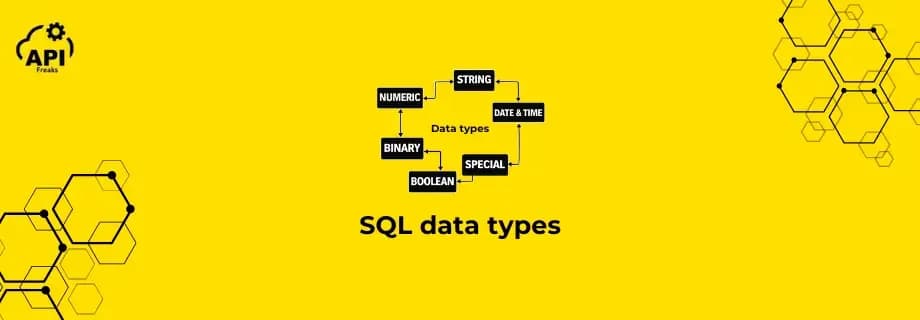
SQL data types define the kind of values you can store in a database column. Choosing the correct data type is important because it affects storage, performance, and data accuracy. Every table column in SQL must have a data type assigned to it. Common SQL Data Types Numeric Data Types 1. INT...

Data Definition Language (DDL) defines and reshapes the structure of a database, its schemas, tables, columns, constraints, indexes, views, sequences, and partitions. Unlike DML (which manipulates row data), DDL changes the blueprint those rows live in. Because DDL alters metadata, it can take strong...
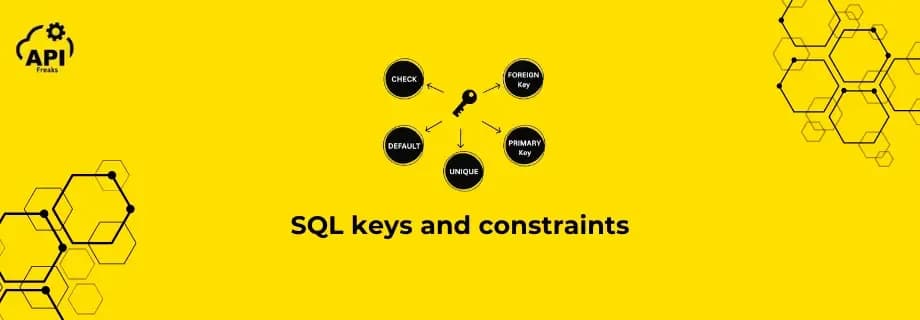
SQL constraints protect data quality. They make sure every row has an ID, and things like email addresses don’t accidentally repeat, so your database stays consistent, reliable, and easy to query. Primary Key * The primary key uniquely identifies each record. * A primary key column can’t be e...

Data Manipulation Language is the part of SQL used to work with the data itself adding it, looking it up, changing it, and removing it. If you think of your database as a set of labeled spreadsheets, DML is how you fill rows in, read them back, edit them, or clear them out. SQL Query is the foundatio...

Filtering and sorting are essential when working with SQL queries. By combining the logical and comparison operators, and sorting techniques, you can retrieve only the data you need and present it in a meaningful order. WHERE Clause - Data Filtering in SQL The WHERE clause filters rows based on ...

In SQL, NULL represents the absence of a value or unknown data. It is not the same as 0 or an empty string. A column can have a NULL value if no data is provided for it. When working with NULL in SQL, it’s important to note that NULL is not equal to anything, not even another NULL. This means that yo...

In SQL, you can combine the results of multiple SELECT queries into a single result set using set operations. The two most common set operators are UNION and UNION ALL. Rules for SQL UNION * Each table used within UNION must have the same number of columns. * The columns must have the same dat...
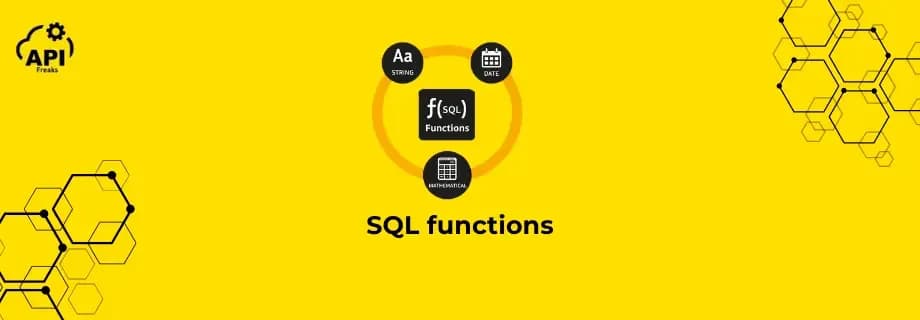
SQL offers a variety of built-in functions to manipulate text, handle dates, and perform mathematical calculations. These functions are widely used for data analysis and transformation. String Functions in SQL String functions help manipulate and format text data stored in your database. UPPER...

In SQL, aggregate functions are used to perform calculations on multiple rows of data and return a single value. These are essential for summarizing, analyzing, and reporting data efficiently. Common Aggregate Functions COUNT: Returns the number of rows that match a specified condition. ...
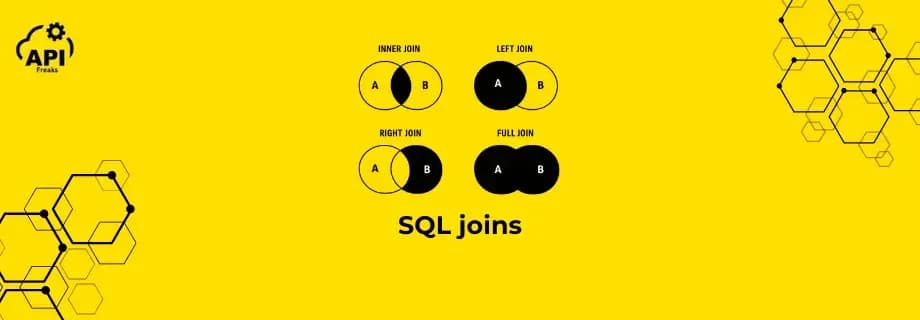
SQL Joins are one of the most important concepts in database management. A SQL Join allows you to combine data from two or more tables based on related columns. In real-world applications, data is rarely stored on a single table. For example, an employees table may store personal information, whil...

A SQL Subquery (also known as a nested query) is a query placed inside another query. It allows you to use the result of one query as input for another, making SQL more flexible and powerful. Subqueries are often used to filter, calculate, or transform data in complex scenarios. * A subquery i...

An SQL View is like a virtual table. It does not store data itself but shows data stored in other tables. Think of it as a saved query that you can reuse anytime. Views help you simplify complex queries, improve security, and make databases easier to work with. Run Reset DB CREATE VIEW emplo...

The SQL CASE statement is a powerful way to add conditional logic inside your queries. Think of it as an “IF–THEN–ELSE” structure within SQL. It allows you to return specific values depending on whether conditions are met, making your queries more flexible and dynamic. Why Use CASE Statements? ...